Petrochemical companies’ needs are extremely diverse. To come out ahead in today’s highly competitive marketplace, producers are striving to improve quality and productivity. Yokogawa provides tailor-made solutions for these needs based on its long and wide-ranging experience in this field.
Challenges
Customer Challenge

Fluctuations in raw material prices and product supply and demand make it absolutely essential to optimize production planning.
Our Solutions

Yokogawa offers a production management system that bridges the gap between planning and manufacturing for optimal scheduling of petrochemical processes.
Enabling Technology

Real-time Production Organizer™ : RPO
Real-time Production Organizer™ (RPO) is a suite of platform applications developed specifically to bridge the gap between production planning and process control, providing a fully integrated business to process (B2P) production environment.

Production Management Solutions from Yokogawa help operations achieve more plant profits and provide a bridge between real-time process systems and corporate systems.
Customer Challenge

To stay competitive in the global market, the optimization of processes throughout a plant is no less necessary than the development of a competitive product offering that meets specific user needs.
Our Solutions

Yokogawa provides plantwide automation solutions that enable the agile and flexible control of petrochemical production workflows and that are fully integrated with a safety instrumented system.
Enabling Technology

Production Control System: CENTUM VP
The CENTUM VP integrated control system secures interruption-free “uptime only” plant performance for optimal productivity and profitability.

Safety Instrumented System: Prosafe-RS
The ProSafe-RS safety instrumented system enables truly integrated solutions while delivering the high availability required for safety integrity level 1-4 (SIL1-4) applications.

vigilantplant services.®
vigilantplant services.® is a suite of comprehensive services that realize Yokogawa's VigilantPlant concept, helping manufacturers achieve safe, reliable, environmentally friendly, and profitable plant operations.

Advanced process control (APC) and online optimization achieve more profitable operations in petrochemical plant. The solutions are available for ethylene, polyethylene, polypropylene and aromatic plants.

Plant resource manager (PRM) makes predictive maintenance easy. Early detection of system and device failure can help prevent catastrophic failure.

Compact, high performance and explosion-proof monitoring cameras exemplify Yokogawa’s commitment to constructing reliable field instruments that are able to withstand even the most severe environments. They are used in a petrochemical plant for monitoring operations day and night.
Customer Challenge

Petrochemical plants consume enormous amounts of energy, so energy saving initiatives at these facilities can go a long way to achieving cost competitiveness and reducing the CO2 emissions that contribute to global warming. One key means by which this can be accomplished is optimizing control of the production process.
Our Solutions

Yokogawa’s advanced process control systems make it possible for plants to operate with increased efficiency, thereby reducing energy consumption and CO2 emissions.
Enabling Technology

Solution-based Software
Integrated, validated and timely operational information supporting continuous improvement initiatives and optimization of production performance.

Highly responsive analytical systems contribute to accurate measurement of product/intermediate property and boiler/furnace combustion, helping petrochemical companies meet tighter quality control and environmental regulations.
Resources
- Stable operation and proactive maintenance were realized at new coal-chemical plant in China.
- Yokogawa engineers ensured a successful and efficient commissioning and startup.
Yokogawa provided an integrated and comprehensive solution for ethylene cracking process optimization.
SMOC APC controller improved control level of ethylene cracking unit and reduced operators workload.
- Operational Excellence by Asset Maximization, Utilizing Yokogawa's DCS, SIS, Analyzers, and Field Instruments.
- The CENTUM VP PCS and ProSafe-RS SIS were integrated using the same engineering environment.
- Nearly 60 gas chromatographs and a large number of other types of analyzers in several analyzer houses.
- Using the CENTUM CS 3000 system, many kinds of plant key performance indexes are calculated and analyzed to produce further improvements.
- During plant start-up, PRM helps the customer's engineers perform all the loop checks.
- Yokogawa provides CENTUM CS 3000, Exaquantum and PRM solutions for China's largest refinery/petrochemical complex.
- Process data management by Exaquantum is a key issue in the petrochemical complex.
- A certified emergency shutdown system
- Substantial reduction in maintenance work
- System configuration with reduced footprint
- System scalability
- Meet the IEC 61508/JIS C 0508 functional safety standards
- Proactively introduce leading edge technologies
- Accommodate the plant licensors' safety, reliability, and maintainability requirements
- Improve the monitoring and operation functions of the emergency shutdown system
Samsung Petrochemical Co. Ltd. (SPCL), a major Korean petrochemical company, produces 700,000 tons per year of purified terephthalic acid (PTA) at its Daesan plant. PTA, a white powder substance that is produced by oxidizing and refining para-xylene, is a precursor to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a polyester material that has excellent thermal resistance and wear resistance and is widely used as a substitute for natural cotton fibers and in film packaging, beverage bottles, tire cords, paints, adhesives, and other applications.
- PetroChina Dushanzi Petrochemicals Polyethylene Plant system migration.
- The revamp included the challenging creation of function design specifications (FDS) as well as FAT and SAT.
- Implementation of multivariable optimizing controllers and robust quality estimators within a record short period
- 3% rise expected in CCR feed amount
- ABS plant migrates from CENTUM XL to integrated CENTUM CS 3000 solution.
- CENTUM CS 3000 Integrated Production Control System together with CCTV equipment, a plant information management system (PIMS), the Exaplog Event Analysis Package, and the CS Batch 3000 package.
- 16,000 FOUNDATION Fieldbus devices
- Main Automation Contractor (MAC)
- DCS anywhere concept integration with site SAP system
- Long term maintenance contract
- Sustainable development
- All logistics of raw materials, intermediate products and final products are controlled and managed by MAS.
- MAS enables Operational Excellence with its seamless interface to enterprise resource planning system.
- Exapilot automates comlex and non-routine decoking process of NCUs.
- Operator workload has been drastically reduced.
- A Japanese petrochemical plant leverages FDT/DTM-compliant intelligent field devices and Yokogawa's PRM asset management system for maintenance efficiency.
- The customer aims to improve maintenance efficiency further by introducing condition-based maintenance (CBM).
- Yokogawa assisted in the project implementation by providing design review, calculation modifications, pre-commissioning, training of operators and engineers, commissioning and post implementation review.
- Shell Global Solutions and Shell Deer Park Management were completely satisfied with the way the project was implemented and with the results achieved.
In the plants of food and beverage manufacturers, there are times when monitoring and recording of production equipment is necessary inside clean rooms. This is an introduction to monitoring and recording in clean rooms using paperless recorders.
Operators must receive diagnostic information before a line block leads to a malfunction. Yokogawa provides predictive diagnostics based on trend analysis of the blocking factor, which improves maintenance efficiency and reduces maintenance costs.
The GX20 and GX90UT offer an average value computation function making it ideal for controlling temperature and other fluctuating phenomena. The operating status can be controlled in real time, providing operating cost reductions.
In limestone-gypsum flue gas desulfurization systems, the consumption of a desulfurization agent (lime) is controlled using online pH analyzers.
If a sensor is not operating, the manufacturer cannot detect moisture in the chlorine and must stop the process. Unfortunately, sensors can deteriorate and deliver inaccurate measurements due to contact with the process.
Fired heaters are used for various processes in oil refining and petrochemical plants.
O2 measurement in hydrocarbon vapor is used for safety monitoring in vacuum distillation columns in petroleum refining. With conventional paramagnetic oxygen analyzers, O2 concentrations are obtained through an extractive sampling system, which conditions the sample prior to being analyzed.
Both bulk and finished inventories are stored in distributed tank farm remote from the site operations. These are difficult to instrument due to the infrastructure cost involved. These are then monitored daily by patrol rounds. While effective, this method does require a large skilled labor force to monitor all of tanks. This can impose an additional risk when the stored medium is of a hazardous nature.
Install a YTMX580 on the side of the rotating furnace that can wirelessly transmit measured values from multiple temperature sensors.
Storage tanks are used in a variety of industries ranging from holding crude oil to holding feedstock for vinyl chloride monomer (VCM).
- Temperature is monitored to maintain consistency of the viscous fiber entering the drum.
- Existing system requires manual temperature readings.
- Wired temperature measurement is not available because the tank is rotating.
- Wireless temperature measurement
Gateway x1, transmitter (YTA) x1, repeater x2 (The 2 repeaters are for redundancy) - Extended antenna to circumvent obstacles and improve the radio path for stable measurement (communication was unstable when the height of the antenna was low).
ISA100 wireless temperature and pressure transmitters with orifice plates allow:
- No cabling installations or maintenance.
- Small amount of hardware and simple equipment implementation means minimizing potential vandalism.
ISA100 Wireless Monitoring
- Gateway x1, Temperature Transmitter (YTA) x3, Pressure Transmitter (EJX) x1, Repeater x1
Gateway is installed at control room and 3m height extended antenna is set.
Industrial Combustion sources such as thermal cracking furnaces and, process heaters play a critical role in the process industry.
- Temperature Transmitter (YTA) and Pressure Transmitter (EJX) are installed at each monitoring point.
- Repeater is installed on high position.
Wastes have been considered to be a serious worldwide environmental problem in recent years. Because of increasing pollution, these wastes should be treated. However, industrial wastes can contain a number of valuable organic components. Recovery of these components is important economically. Using conventional distillation techniques, the separation of acetic acid and water is both impractical and uneconomical, because it often requires large number of trays and a high reflux ratio. In practice special techniques are used depending on the concentration of acetic acid.
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), or also known as LP Gas or auto gas, is a mixture of hydrocarbon gases used as a fuel in heating appliances and vehicles, and increasing replacing chlorofluorocarbons as an aerosol propellant and a refrigerant to reduce damage to the ozone layer.
Pressure measurement of tubeless tyres to monitor the air loss is one of the key performance tests in the tyre manufacturing units. Relocation of tyres from one testing rack to the other for various tests and frequent movement of the testing setup for conditional tests to various locations calls for cable free implementation for ease of handling.
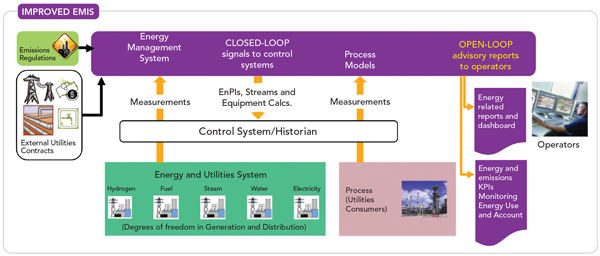
Visual MESA© is a steam system optimization and management computer program that was originally developed at Chevron and now marketed by Nelson & Roseme, Inc. Visual MESA is currently used at refinery and chemical manufacturing sites to optimize the overall site steam system and the parts of the electrical system that economically trade off with the steam system.
This paper will explore significant optimization variables and constraints commonly encountered in refinery steam system optimization, the strategies Visual MESA uses to deal with them.
In general, refineries exhibit a very good potential for real time monitoring and optimization using Visual MESA Energy Management System.
Based on our extensive experience, overall benefit in the range of 2% to 5% of the total energy cost can be achieved. Expected project payback is always less than one year.
Outline
- Introduction
- What is Energy Optimization
- How does a Real Time Online Energy Management System based on Visual MESA work
- Calculation Foundation for Key Performance Indicators
- Visual MESA implementation at Saudi Kayan (A SABIC Affiliate) (SK)
- Optimization Actionable Items
- Economic Benefits
- Relevance of Visual MESA RTEMS for SK's Sustainability Initiative
- Conclusions
This paper will not describe just all the features of the software or fully explain on-line optimization technology. The objective of this work is to present some interesting facts and lessons from the experience of implementing a cost based optimization program at thirty oil refineries and petrochemical complexes, around the world, since 1997. This paper will focus on the key optimization variables and constraints in steam system optimization, how they should be handled and how the human and organizational aspects can be addressed.
Industrial facilities where power and steam is produced (i.e., Cogeneration) exhibit a very good potential for real time monitoring and optimization using Visual MESA Energy Management System.
Based on our extensive experience, overall benefit in the range of 2% to 5% of the total energy cost can be achieved. Expected project payback is always less than one year.
Visual MESA was successfully applied to many industrial facilities worldwide, several of them operating steam and power generation networks of different complexity and capacity but all with energy cost savings.
This paper discusses real industrial examples in which the sitewide utilities system of refinery and petrochemical Sites are optimized with a real time, on line, industrially proven software. Experiences gained during more than 20 years of industrial projects deployed worldwide are commented (Refs. 1 to 10 are related to some recent projects). Main project steps are explained and critical details to be taken into account to assure successful use and proper technology transfer are presented. Specific case studies will be discussed in the paper.
Utilities and energy systems are often the major source of SOx, NOx and CO2 emissions, therefore, emissions control and the management of credits and quotas are tightly interrelated with energy management.
In the case of refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants, energy represents the main cost (second to feedstock) and therefore its reduction has become a bottom line business decision. The energy systems at these sites are inherently complex, with the emissions cost analysis and limits compliance introducing an additional factor to the complexity of the energy costs reduction challenge.
Process plants use different type of fuels, they often operate cogeneration units, their steam networks consist of several pressure levels, there are different types of energy consumers and there are emission limits to be observed. Import or export of electricity in deregulated markets, which could also be traded off with more or less CO2 and other contaminant gaseous emissions, increase the optimization problem complexity.
This paper addresses some of the root causes for issues and discusses the best practices that will help to avoid project failures. Main project steps are explained and critical details to be taken into account to assure successful use and proper technology transfer are discussed. It also presents real industrial examples in which the whole utilities system cost of a production Site (i.e., steam, fuels, boiler feed water and electricity) is optimized with a real time, online, industrially well established software.
Utilities and energy systems are often the major source of SOx, NOx and CO2 emissions, therefore, emissions control and the management of credits and quotas are tightly interrelated with energy management. In the case of refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants, energy represents the main cost (second to feedstock) and therefore its reduction has become a bottom line business decision. The energy systems at these sites are inherently complex, with the emissions cost analysis and limits compliance introducing an additional factor to the complexity of the energy costs reduction challenge.
The energy systems, the steps for the implementation of Visual MESA and several features of the model are described in this article, with a focus on the use of the software for the calculation of energy-related KPIs. The EMS implementation project is discussed and the main conclusions relative to the reduction in operating costs are also presented.
Experiences gained during more than 20 years of industrial projects deployed worldwide are commented. Main project steps are explained and critical details to be taken into account to assure successful use and proper technology transfer are presented. Specific case studies will be discussed in the paper. Open loop vs Closed loop implementation is also presented.
Rohm and Haas Company is one of the world's largest manufacturers of specialty materials, including adhesives, sealants, coatings, monomers, electronic materials, inorganic and specialty solutions, and ion exchange resins. Founded in 1909 by two German entrepreneurs, Rohm and Haas has grown to approximately $6 billion in annual revenues.
Alarm management is not just a project that has a start and end date; it's a continuous cycle. Once the alarm system has been reviewed and improvements have been identified, we must check that controls are in place to ensure the alarm system remains functional. The key is to ensure that the system is continuously monitored and any changes are fully documented. There are seven key steps for alarm management. Rationalization is one of those critical steps.
This paper shows how to improve distillation operations by focusing on procedure automation. It will review the importance of using procedures in distillation operations and highlights the collaboration work underway between Fractionation Research Inc. (FRI) and Yokogawa Corporation to improve procedural operations.
The worlds of process automation and production management have been converging for some time. What once used to be islands of automation and production management functionality connected through highly proprietary integration schemes that were costly to maintain have developed into integrated platforms that provide seamless data exchange between the world of automation and the plant floor, the functions of production and operations management, and integration with business level systems.
The world of process automation is governed by procedures. While we like to refer to the process industries as being largely "continuous", this could not be further from the truth. Process manufacturing is constantly in flux.
From engineering to installation, commissioning, operations, and maintenance, FOUNDATION fieldbus offer significant cost reductions of 30 percent or more versus conventional analog systems. Many of these cost reductions come from the advanced functions that fieldbus offers versus analog technology.
The automation suppliers that will be successful in the long term will be those that effectively address application or industry specific problems for end users with a value proposition that cannot be ignored. These problems exist throughout the process industries today, and they won't be solved by simply offering a product, but through a combination of hardware, software, services, application expertise, and knowledge.
In ARC's view, customers need a compelling business value proposition to justify investment in any kind of automation. Vigilance and VigilantPlant were created with this in mind. Yokogawa's vision with VigilantPlant is to create an environment where plant personnel and operators are well informed, alert, and ready to take action.
Yokogawa has come a long way in making its message clear to the world of process automation. Last year, the company embarked on a full-scale global marketing campaign to make customers aware of the company's focus on system reliability, security, dependability, and robustness. Dubbed "Vigilance", the campaign created a unified message for the company and greatly helped expand awareness of the Yokogawa brand and corporate philosophy.
Process automation end users are under more pressure than ever to do more with less. The current economic climate means that many automation capital projects are on hold. With capital budgets tighter than ever, users instead focus on operational budgets (where cost cutting is also a key concern), or on automation investments with a very rapid return on investment.
In today's dynamic industrial marketplace, the only constant is change. Raw material costs, energy costs, market demands, environmental and safety regulations, technology, and even the nature of the labor force itself are constantly changing, and not always in predictable directions.
Migration of a refinery's DCS provided an opportunity to reconfigure and consolidate the control rooms and operational management system.
July 2011
Process plants are run according to operational procedures. These procedures consist of a set of tasks that are executed in a consistent manner to achieve a specific objective, such as starting up, shutting down or transitioning a unit as part of making a product.
September 2008
Yokogawa is helping a large chemicals site in China manage product transfer by road, ship and pipeline.
March 2006
The new CSPC (CNOOC and Shell Petrochemicals Company Limited) petrochemical complex at Daya Bay in southern China is one of the world's largest process industry projects (see box, Figure 1 and Table). It has a control system to match. Process Worldwide spoke to Johan Veerman, principal instrument and process control engineer at CSPC, about the challenges of managing such a huge job.
CONTROL, January 2013
Standard Automation Methodology Improves Operations and Prevents Incidents by Enabling the Sharing of Best Practices Among Operators.
ARC believes that by implementing procedural automation, many process plants can minimize variability to help ensure smooth, efficient, and safe state transitions.
Adding process considerations improves energy savings and production performance.
Downloads
Brochures
Videos
The YSS1000 setting software (hereinafter referred to as the YSS1000) is package software to configure the functions of the YS1000 series (hereinafter referred to as the YS1000) devices. Writing and reading of parameters and user programs of the YS1000, and PID tuning and monitoring of user programs can be performed through the use of communication.
Chet Mroz, President & CEO Yokogawa North America, discusses the benefits of IoT at the 2015 ARC Industry Forum in Orlando.
News
-
Press Release Feb 20, 2023 Yokogawa Enters into Partnership with Radial Software Group to Provide AI-powered Viewport Software Worldwide
- Giving customers a single view of all their technical data -
Looking for more information on our people, technology and solutions?
Contact Us