Introduction
Two types of polymerization reaction are used to produce styrene-butadiene copolymers, the emulsion type and the solution type. This section addresses volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from the manufacture of copolymers of styrene and butadiene made by emulsion polymerization processes. The emulsion products can be sold in either a granular solid form, known as crumb, or in a liquid form, known as latex.
Copolymers of styrene and butadiene can be made with properties ranging from those of a rubbery material to those of a very resilient plastic. Copolymers containing less than 45 weight percent styrene are known as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). As the styrene content is increased over 45 weight percent, the product becomes increasingly more plastic.
As shown in below figure, fresh styrene and butadiene are piped separately to the manufacturing plant from the storage area. Polymerization of styrene and butadiene proceeds continuously through a train of reactors, with a residence time in each reactor of approximately 1 hour. The reaction product formed in the emulsion phase of the reaction mixture is a milky white emulsion called latex. The overall polymerization reaction ordinarily is not carried out beyond a 60 percent conversion of monomers to polymer, because the reaction rate falls off considerably beyond this point and product quality begins to deteriorate.
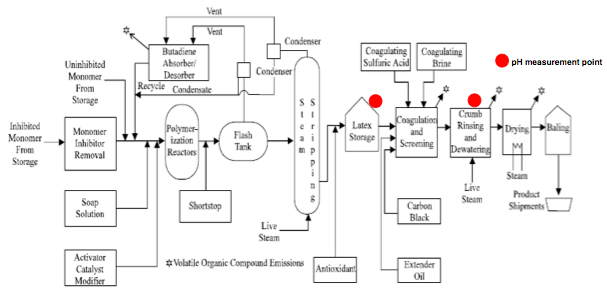
Because recovery of the unreacted monomers and their subsequent purification are essential to economical operation, unreacted butadiene and styrene from the emulsion crumb polymerization process normally are recovered. The latex emulsion is introduced to flash tanks where, using vacuum flashing, the unreacted butadiene is removed. The butadiene is then compressed, condensed, and pumped back to the tank farm storage area for subsequent reuse. The condenser tail gases and noncondensables pass through a butadiene adsorber/desorber unit, where more butadiene is recovered.
Some noncondensables and VOC vapors pass to the atmosphere or, at some plants, to a flare system. The latex stream from the butadiene recovery area is then sent to the styrene recovery process, usually taking place in perforated plate steam stripping columns. From the styrene stripper, the latex is stored in blend tanks.
From this point in the manufacturing process, latex is processed continuously. The latex is pumped from the blend tanks to coagulation vessels, where dilute sulfuric acid (H2SO4 of pH 4 to 4.5) and sodium chloride solution are added. The acid and brine mixture causes the emulsion to break, releasing the styrene-butadiene copolymer as crumb product. The coagulation vessels are open to the atmosphere. Leaving the coagulation process, the crumb and brine acid slurry is separated by screens into solid and liquid. The crumb product is processed in rotary presses that squeeze out most of the entrained water. The liquid (brine/acid) from the screening area and the rotary presses is cycled to the coagulation area for reuse.
Typical Process Details:
 Fluid: Crumb slurry
Fluid: Crumb slurry
- Fluid composition (normal):
Water: 95% wt
Polymer: 4.06% wt
Fatty acid: 0.2% wt
Extender oil: 0% wt. (Max. 1.45% wt)
Rosin acid: 0.078%wt - Acidity (min/orm/Max): 0.0/3.6/14.0
- Fluid design conditions P@T: 1.033 Kg/cm2- g@115 degC
- Boiling point @ operating pressure: 100 degC
Dew point @ operating pressure: 100 degC
Boiling point @ atmospheric pressure: 100 degC
Dew point @ atmospheric pressure: 100 degC - Density: 980 kg/m3 (Norm)
- Fluid able to foul
Max. pressure: 1.033 kgf/cme-g Tempe: 62 degC
Crumb rinsing and dewatering
Typical Problems:
This is indeed a tough application. The rubber tends to stick on the holder. The rubber does not tend to stick on the glass very much.
Remedies:
To mount the holders in such a way that they can swing with the process flow and make them easy to remove for manual cleaning: 0.5 or 1 m immersion fittings hanging on the hoisting cable on a hook.
Solutions:
- Sensor: SC25V series
- Features SC25V
- External titanium Liquid Earth
- Pt1000 integration in pH compartment giving highly accurate temperature compensation
- CIP and Steam cleaning possible Large internal KCl volume giving the sensor a longer life time
- SC25V-ALP25 for chemically harsh applications and high temperatures
Sensor Holder:
The FD20-P37 comes with hoisting cable made of SS316. When the holder is mounted this way, just hangs in the vessel, then it can swing with the flow. Otherwise the rubber slurry may damage the sensor if the holder is mounted rigidly. Most probably the sensor protection cage must be removed to prevent the polymer to fill the cage.
Related Industries
-
Bulk & Petrochemical
Whether you produce petrochemicals, inorganics or intermediates, chemical companies are under cost and margin pressures to deliver products in a timely and efficient manner while maintaining safe and compliant operations. Additionally, chemical companies need to adjust to fluctuating feedstock and energy prices and to provide the most profitable product mix to the market.
Yokogawa has been serving the automation needs of the bulk chemical market globally and is the recognized leader in this market. With products, solutions, and industry expertise, Yokogawa understands your market and production needs and will work with you to provide a reliable, and cost effective solution through the lifecycle of your plant.
-
Petrochemical
Petrochemical companies’ needs are extremely diverse. To come out ahead in today’s highly competitive marketplace, producers are striving to improve quality and productivity. Yokogawa provides tailor-made solutions for these needs based on its long and wide-ranging experience in this field.
Related Products & Solutions
-
12mm pH Sensor SC25V
The SC25V is a pH sensor in a 12 mm design that includes an integral temperature element and a Liquid earth electrode.
-
2-Wire Transmitter/Analyzer FLXA202
The FLEXA™ series analyzers are used for continuous on-line measurements in industrial installations. With an option for single or dual sensor measurement, they are the most flexible two-wire analyzer available.
-
2-Wire Transmitter/Analyzer FLXA21
The FLEXA™ series analyzers are used for continuous on-line measurements in industrial installations. With an option for single or dual sensor measurement, they are the most flexible two-wire analyzer available.
-
Digital SMART SENCOM™ Adapter, SA11
Reusable SMART adapter, requiring only the analog sensor to be disposed of when it reaches the end of its lifetime. With the SENCOM 4.0 platform, Yokogawa delivers reduced costs and waste while contributing to its long-term business goals of a sustainable future for all.
-
Immersion Holder FD20
The immersion fittings are designed for either pH or ORP (Redox) measurements in tanks, open vessels and drains. They have a "hoisting cable" for easy maintenance.
-
Liquid Analyzers
Liquid analyzers are used for monitoring process chemistry including water quality, providing process optimization and control.
-
Multi Channel 4-Wire Analyzer FLXA402
The FLEXA™ series analyzers are modular-designed analyzers used for continuous online measurements in industrial installations. They offer single or multi-sensor measurement.
-
pH and ORP Analyzers
pH and ORP meters, analyzers and transmitters are used for continuous process monitoring of pH and ORP to ensure water/product quality, monitor effluent discharge, batch neutralization, pulp stock, scrubbers, cooling towers, chemical, water/wastewater treatment and many other applications.